Overview
This is an in-progress case study to provide early results of a field trial to establish a significant white pine component in multi-aged mixed pine-hardwood stands through overstory density management.
There is often abundant natural white pine regeneration present on these native plant communities in this part of the state, but very little of it recruits into larger size classes without some sort of silvicultural assistance. Therefore, we wanted to try several different overstory densities to see what density (or densities), and therefore forest floor light conditions, best helped to facilitate recruitment of white pine to larger size classes.
Our study area includes 9 stands. We tried 3 different management regimes to achieve different overstory densities, and forest floor light conditions.
We are sharing very early results and observations now, with the intent of updating the study over time as we continue to monitor and manage the sites.
Silviculture Objectives
- Establish or maintain uneven aged pine-mixed hardwood stands with a significant white pine component through overstory density management, using a natural regeneration strategy.
- Maintain or enhance the native plant community (S2 NPC).
- Keep more of a mature, intact canopy for interior forest habitat purposes.
- Increase white pine regeneration recruitment into sapling and larger size classes.
Pre-treatment stand description and condition
Stand establishment and management history
Veteran staff think that the pine areas probably originated after a stand-replacing fire between 1850 and 1920, and that some of the other areas of the stand may have been harvested in the late 1800s which regenerated more heavily to hardwoods.
Table 1: MNDNR FIM forest inventory stand numbers and forest type labels for the 9 stands in the case study
FIM Inventory Stand Number | FIM Inventory Forest Type, Size and Density Labels |
T13230w1321357 1357 | White Pine 66 |
T13230w1321394 1394 | Norway Pine 59 |
T13230w1321417 1417 | Oak 56 |
T13230w1321441 1441 | Norway Pine 67 |
T13230w1321451 1451 | Aspen 56 |
T13230w1321404 1404 | Aspen 57 |
T13230w1321466 1466 | Norway Pine 56 |
T13230w1321421 1421 | Norway Pine 57 |
T13230w1321426 1426 | Norway Pine 77 |
Pre-treatment species composition
There were 3 general types of stands:
- The largest harvest block was dominated by white pine, with significant components of red pine, bigtooth aspen, red oak, and more minor amounts of quaking aspen, bur oak, and mixed maple, basswood, paper birch, black cherry. Regeneration included extremely abundant small white pine, as well as components of several other species, including sugar maple and ironwood from 1” DBH to 5” DBH (Table 2).
- The small pine clearcut was mostly red pine, with some white pine and maple mixed in. Regeneration included very abundant small white pine, as well as small amounts of several other species, including a sugar maple component from 1” DBH to 3” DBH (Table 3).
- The hardwood clearcut gaps were hardwood mixes with red oak, aspen species, maple species, with lesser amounts of basswood, paper birch, and scattered bur oak, white pine and red pine. Regeneration included abundant small white pine, as well as components of several other species, including a significant ironwood component from 1” DBH to 5” DBH (Table 4).
Table 2: Pre-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 1: Area to be selectively thinned in a variable manner to create some small gaps and also some uniform thinning – 39 acres
Treatment 1 - Pre-Treatment Regeneration Data - September, 2015 | ||||
| Stems/acre by size class | |||
Species | <1' tall | (<1"dbh, >1' tall) | (1-3"dbh) | (3-5"dbh) |
Basswood | 167 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
Black Cherry | 56 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Green Ash | 56 | 56 | 0 | 0 |
Elm | 0 | 0 | 0 | 6 |
Ironwood | 56 | 611 | 222 | 33 |
Northern Red Oak | 111 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Red Maple | 2,556 | 0 | 0 | 28 |
Sugar Maple | 722 | 333 | 83 | 28 |
White Pine | 284,389 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Total | 288,113 | 1,000 | 305 | 106 |
Table 3: Pre-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 2: Clearcut all species in small gap to release desirable advance regeneration – 0.3 acres. Only one gap was created in a small stand dominated by pine.
Treatment 2 - Pre-Treatment Regeneration Data - October, 2015 | ||||
| Stems/acre by size class | |||
Species | <1' tall | (<1"dbh, >1' tall) | (1-3"dbh) | (3-5"dbh) |
Big-tooth Aspen | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
Northern Red Oak | 200 | 0 | 0 | 00 |
Red Maple | 0 | 0 | 0 | 20 |
Sugar Maple | 1,000 | 200 | 600 | 0 |
Trembling Aspen | 0 | 0 | 0 | 40 |
White Pine | 77,800 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Total | 79,000 | 200 | 600 | 80 |
Table 4: Pre-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 3: Clearcut all hardwoods and reserve all pine to create large gaps with pine seed trees – 6.1 acres
Treatment 3 - Pre-Treatment Regeneration Data - October, 2015 | ||||
| Stems/acre by size class | |||
Species | <1' tall | (<1"dbh, >1' tall) | (1-3"dbh) | (3-5"dbh) |
Black Cherry | 0 | 48 | 0 | 0 |
Green Ash | 0 | 48 | 0 | 5 |
Ironwood | 48 | 95 | 310 | 29 |
Northern Red Oak | 48 | 95 | 24 | 0 |
Paper Birch | 0 | 48 | 0 | 5 |
Red Maple | 3,190 | 0 | 48 | 33 |
Sugar Maple | 143 | 0 | 0 | 10 |
Trembling Aspen | 48 | 143 | 48 | 5 |
White Pine | 9,714 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
Total | 15,207 | 477 | 430 | 87 |
Pre-treatment growth and stocking
Table 5: 09/28/2018 appraised timber volume estimates (cords)
Species | Product | Volume |
Aspen Species | Woodsrun Cordwood | 243.0 |
Mixed Species* | Woodsrun Mixed Products | 207.0 |
White Pine | Woodsrun Mixed Products | 118.0 |
Norway Pine | Woodsrun Mixed Products | 82.0 |
Total |
| 650.0 |
*Mixed species includes: Sugar maple, red maple, paper birch, red oak, aspen, bur oak and basswood.
Landowner objectives/situation
Camp Ripley lands are managed under strategic direction outlined in the Camp Ripley Sentinel Landscapes Management Plan. A specific objective for white pine management on Camp Ripley lands is to maintain or increase the amount of it.
Note: Historically, white pine most often occurred as a component in other forest types rather than as a pure type. It is most successfully introduced in stands with some residual overstory; therefore, reaching this goal may not actually affect a significant change in the number of acres of white pine cover type.
Silviculture Prescription
The following series of treatments were implemented:
Treatment | Date | Description | Acres |
Silvicultural assessment | 2015 | This area is a mix of mature hardwoods and conifers. This stand will use variable density management to mimic natural ecology. This area will be turned into a multi aged stand and managed through uneven age management techniques. |
|
Variable density retention thinning harvest Permit B013113 | 2018 | Treatment type #1 – variable density retention thinning in white/red pine stands, ranging from 80-190 residual BA with an average of 128. | 35
|
Uniform density thinning harvest Permit B013113 | 2018 | Treatment type #1 – standard, uniform density retention thinning in pine stand, reducing BA to 90 sq ft. | 4.1 |
Small gap clearcut harvest Permit B013113 | 2018 | Treatment type #2 – small gap clearcut harvest in a red/white pine stand. Only one gap was cut. | 0.3 |
Gap clearcut of hardwoods with pine seed trees reserved Permit B013113 | 2018 | Treatment type #3 – gap clearcuts of hardwoods reserving pine seed trees. 5 gap areas totaling 6.1 acres. | 6.1 |
What actually happened during the treatment
A cut-to-length operation was used. Operations went well. Approximately 3 years post-harvest a windstorm came through the area toppling over a few acres throughout the treatment area, with many large pine coming down.

Figure 1: Pine logs from the harvest operation in 2018
Post-treatment assessment
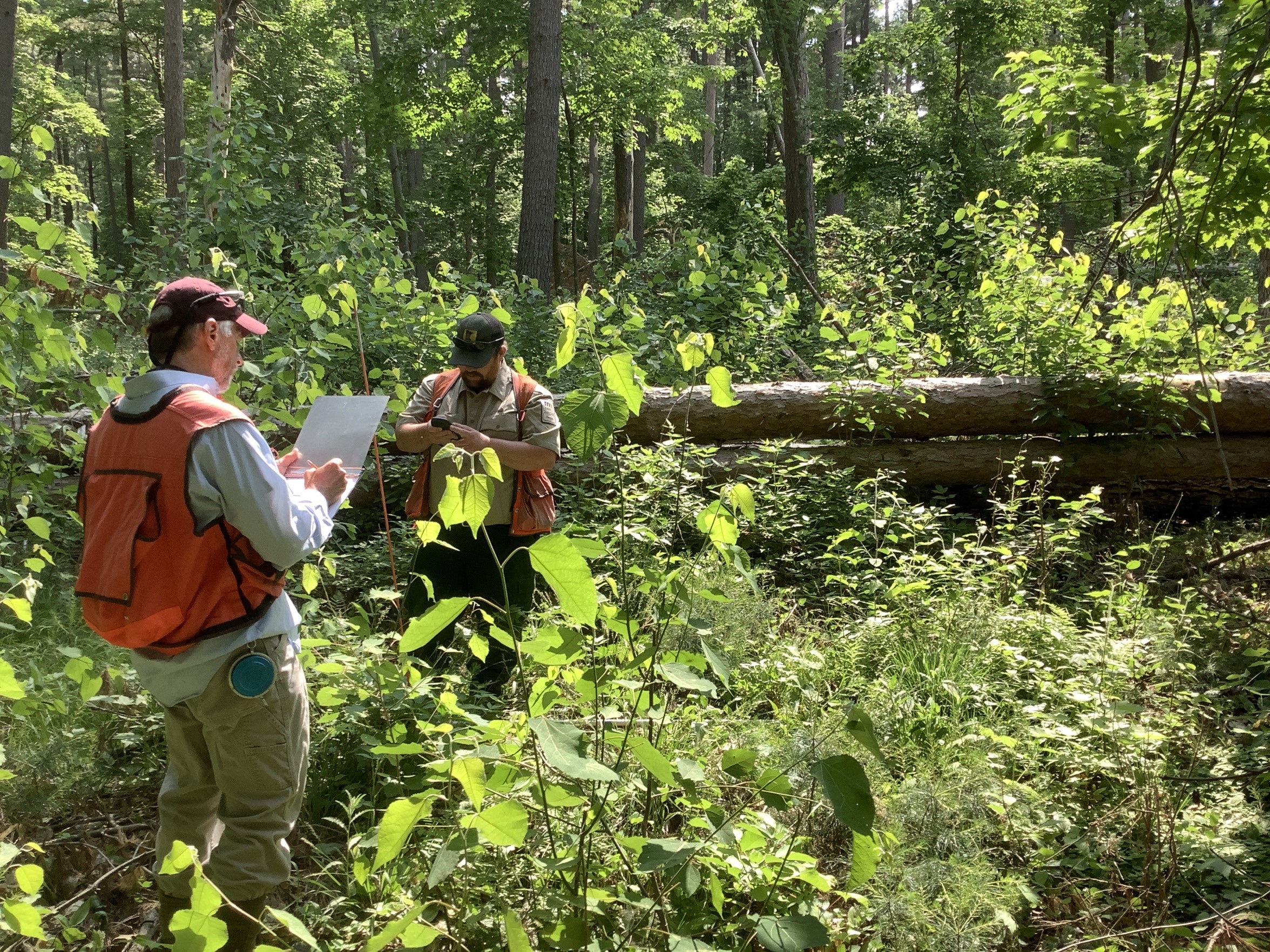

Figure 2: Gathering regeneration data in June 2023 in a clearcut patch
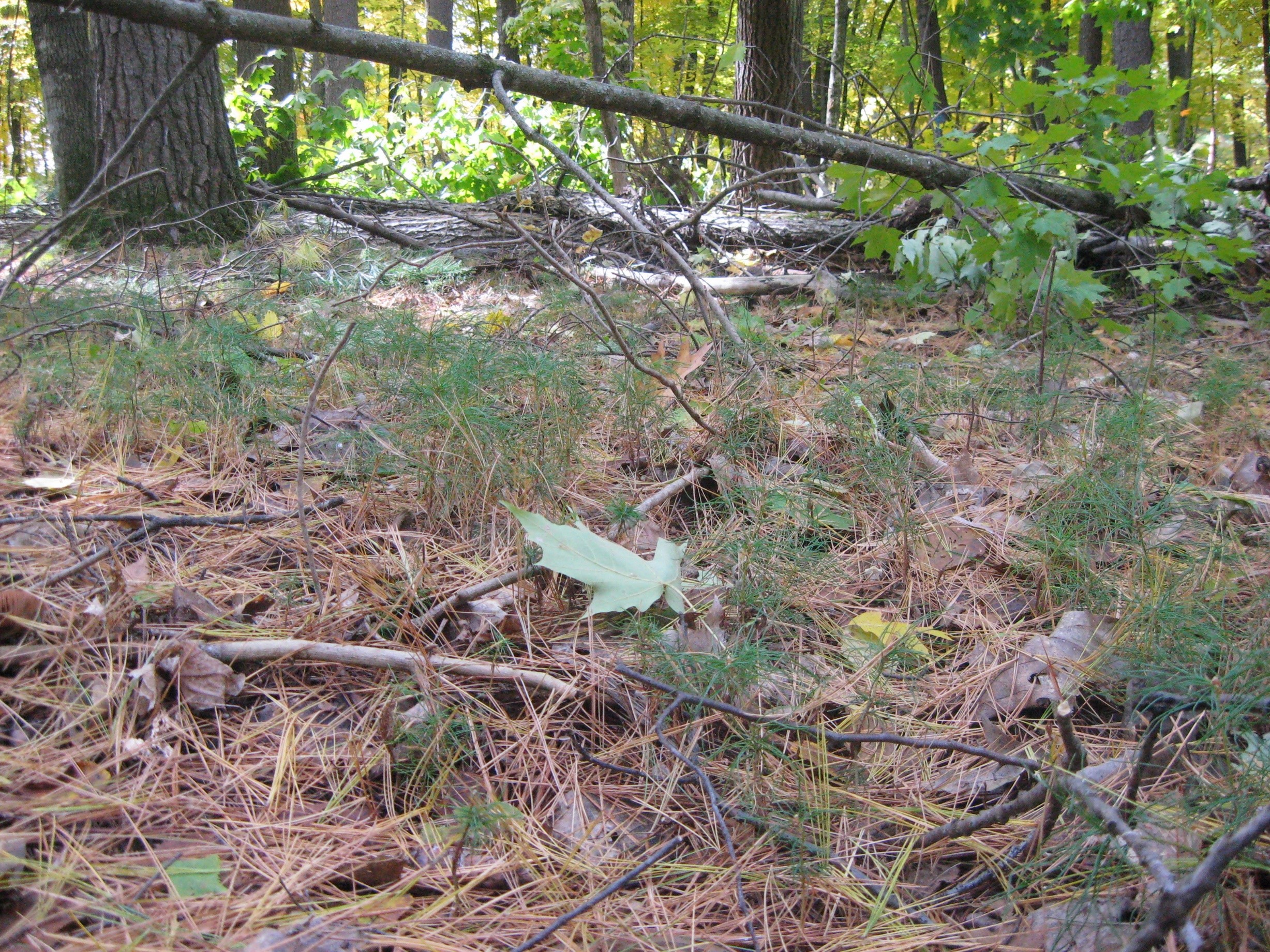

Figure 3: Abundant white pine seedlings in June 2023 in a portion of the variable density thinning treatment
3 key observations as of 2023 (See Tables 6, 7 and 8)
- White pine regeneration is most abundant and well-distributed by far on treatment area 1 – variable density and uniform density pine thinning. To be clear, there was more pre-treatment white pine regeneration in this treatment area to begin with. The thinning has provided more light at the surface to enable greater growth and recruitment of existing small white pine regeneration, and also to enable additional establishment of new seedlings after a good seed crop year.
- White pine regeneration is least abundant and distributed on treatment area 3 – Clearcut all hardwoods and reserve pine to create large gaps with pine seed trees.
- Heavy vegetative competition that has occupied treatment areas 2 and 3 - the small to large pine clearcut areas - has resulted in conditions of heavy competition for white pine regeneration that will require silvicultural assistance soon. The objective of the silvicultural work will be to enable a white pine component to achieve more consistent distribution, and to recruit to larger size classes. Assistance will consist of killing competing vegetation with herbicide, and possibly supplemental planting of white pine seedlings.
Table 6: Initial post-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 1 in 2023. Freq = frequency on plots
Treatment: Area selectively thinned in a variable manner to create some small gaps, and also some uniform density retention thinning. 39 total acres
Size Class | < 1’ tall | ≥1’ tall and < 1” DBH | 1” to 3” DBH | 3” to 5” DBH | ||||
Species | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq |
Bigtooth Aspen | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 38 | 8% | 0 | 0% |
Basswood | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Black Cherry | 77 | 8% | 308 | 23% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Ironwood | 0 | 0% | 154 | 8% | 38 | 8% | 0 | 0% |
Northern Red Oak | 615 | 38% | 231 | 15% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Paper Birch | 0 | 0% | 154 | 15% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Red Maple | 5,769 | 85% | 923 | 54% | 0 | 0% | 23 | 23% |
Red Pine | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Sugar Maple | 154 | 8% | 1,077 | 38% | 38 | 8% | 8 | 8% |
Trembling Aspen | 0 | 0% | 1,000 | 54% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
White Pine | 6,308 | 92% | 4,231 | 69% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Total Stems/Acre | 12,923 |
| 8,078 |
| 114 |
| 31 |
|
Table 7: Initial post-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 2 in 2023. Freq = frequency on plots
Treatment: Clearcut all species in small gap to release desirable advance regeneration. 0.3 acres
Size Class | < 1’ tall | ≥1’ tall and < 1” DBH | 1” to 3” DBH | 3” to 5” DBH | ||||
Species | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq |
Bur Oak | 200 | 20% | 400 | 20% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Northern Red Oak | 400 | 20% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Red Maple | 3,400 | 100% | 1,000 | 60% | 100 | 20% | 40 | 20% |
Red Pine | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Trembling Aspen | 0 | 0% | 600 | 20% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
White Pine | 2,000 | 60% | 800 | 60% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Total Stems/Acre | 6,000 |
| 2,800 |
| 100 |
| 40 |
|
Table 8: Initial post-treatment regeneration data by size class for treatment type 3 in 2023. Freq = frequency on plots
Treatment: Clearcut all hardwoods and reserve pine to create large gaps with pine seed trees – 6.1 acres
Size Class | < 1’ tall | ≥1’ tall and < 1” DBH | 1” to 3” DBH | 3” to 5” DBH | ||||
Species | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq | Stems/ Acre | Freq |
Black Cherry | 0 | 0% | 143 | 5% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Ironwood | 0 | 0% | 238 | 14% | 95 | 14% | 0 | 0% |
Northern Red Oak | 476 | 29% | 190 | 14% | 24 | 5% | 0 | 0% |
Paper Birch | 0 | 0% | 667 | 24% | 48 | 5% | 0 | 0% |
Red Maple | 2,667 | 62% | 1,571 | 67% | 143 | 14% | 19 | 14% |
Red Pine | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Sugar Maple | 0 | 0% | 95 | 10% | 0 | 0% | 5 | 5% |
Trembling Aspen | 0 | 0% | 1,524 | 14% | 4,229 | 67% | 0 | 0% |
White Pine | 762 | 33% | 1,000 | 38% | 0 | 0% | 0 | 0% |
Total Stems/Acre | 3,905 |
| 5,428 |
| 4,539 |
| 24 |
|
We plan to periodically update this case study moving forward
These are very early results. We intend to update this case study periodically as we continue to monitor regeneration until adequate white pine regeneration recruits to the point where they are “free to grow”.
Plans for future treatments
- For treatment areas 2 and 3 - small to large pine clearcut areas after harvest: Treat competing vegetation with herbicide, and possibly supplemental planting of white pine seedlings The objective of the silvicultural work will be to enable a white pine component to achieve more consistent distribution, and to recruit to larger size classes.
- Future thinning/small gap/ clearcut with reserves harvest to maintain and enhance a diverse, multi-age stand structure forest.
Costs and economic considerations
Costs
Timber sale administration: $125/acre (2019 dollars)
Total costs: $125/acre (2019 dollars)
Revenue
Timber revenue: $397/acre
Total revenue: $397/acre (2019 dollars)
Other notes
We gratefully acknowledge the review and editing assistance of MNDNR Silviculture Program Consultant Mike Reinikainen.
Summary / lessons learned / additional thoughts
3 key observations as of 2023
- White pine regeneration is most abundant and well-distributed by far on treatment area 1 – variable density and uniform density pine thinning.
- White pine regeneration is least abundant and distributed on treatment area 3 – Clearcut all hardwoods and reserve pine to create large gaps with pine seed trees.
- Heavy vegetative competition that has occupied treatment areas 2 and 3 - the small to large pine clearcut areas after harvest - has resulted in conditions of heavy competition for white pine regeneration that will require silvicultural assistance soon. The objective of the silvicultural work will be to enable a white pine component to achieve more consistent distribution, and to recruit to larger size classes. Assistance will consist of killing competing vegetation with herbicide, and possibly supplemental planting of white pine seedlings.
These are very early results - we plan to periodically update this case study moving forward
We intend to update this case study periodically with updated data and analysis, as we continue to monitor regeneration until adequate white pine regeneration recruits to the point where they are “free to grow”.
Supplemental content
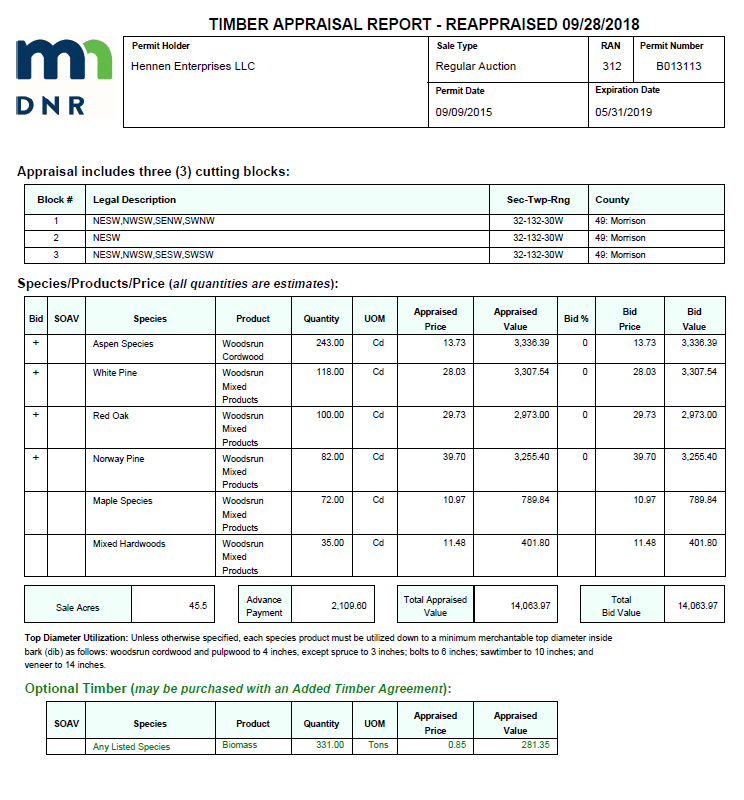
Supplemental figure 1: Page 1 of timber sale appraisal
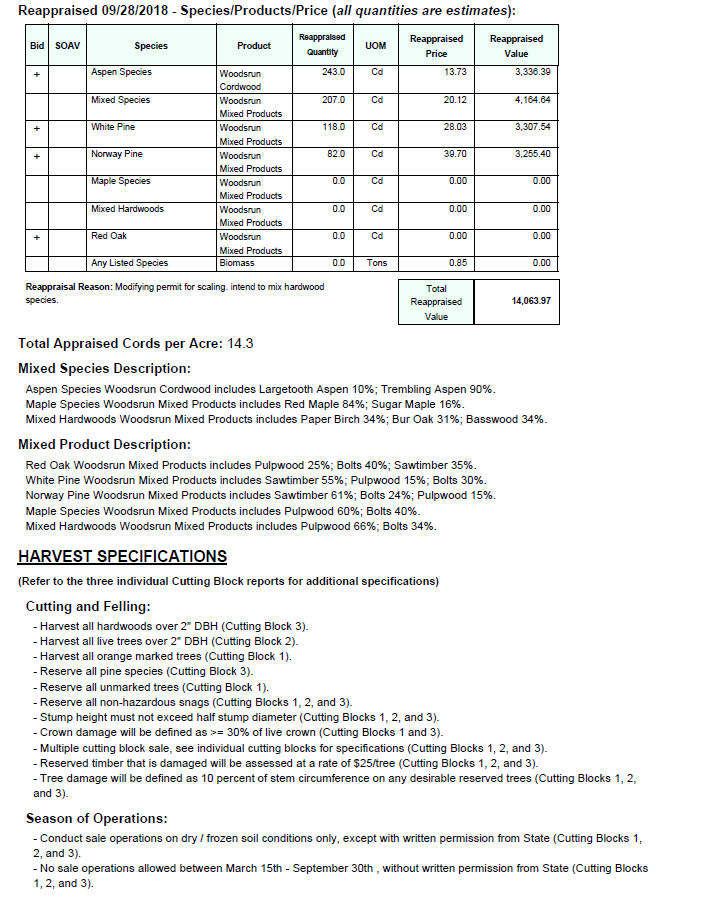
Supplemental figure 2: Page 2 of timber sale appraisal
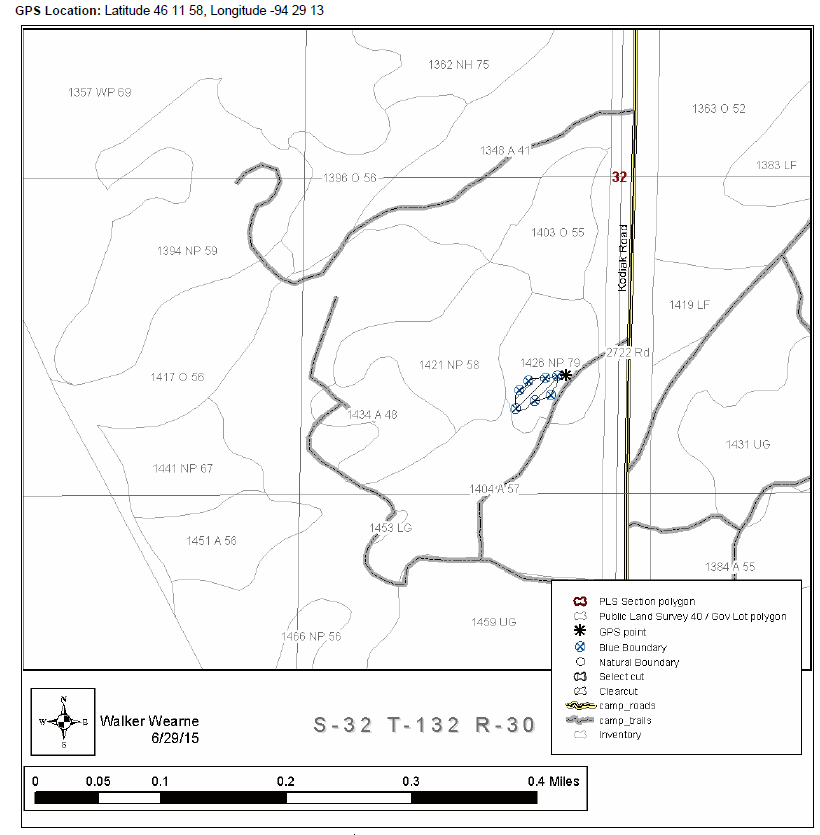
Supplemental figure 3: Map of cutting block 1 from the timber sale appraisal
Supplemental figure 4: Map of cutting block 2 from the timber sale appraisal
Supplemental figure 5: Map of cutting block 3 from the timber sale appraisal

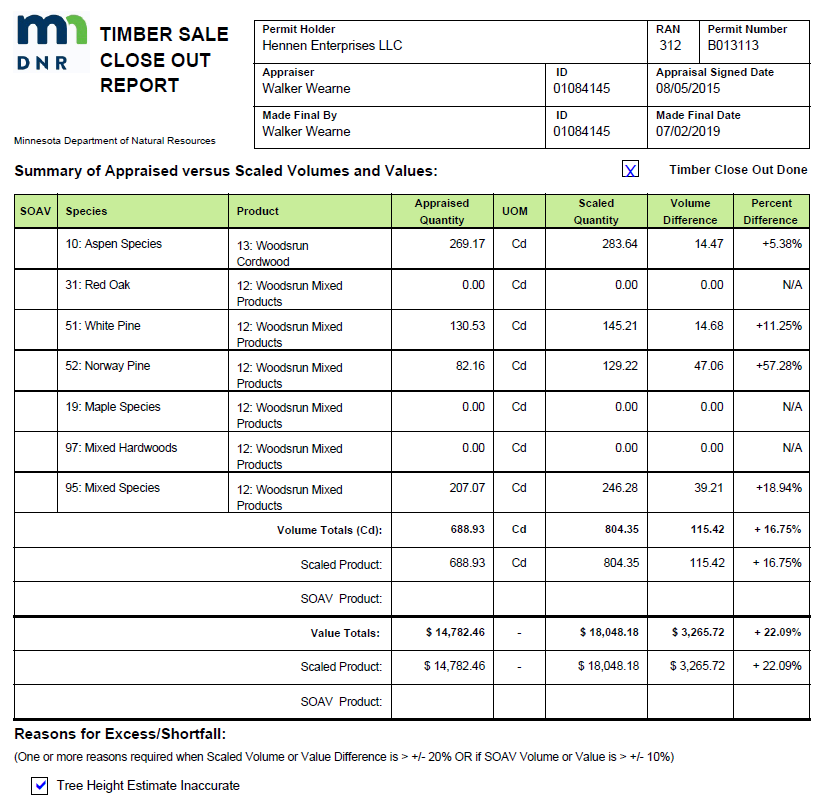
Supplemental figure 6: Timber sale closeout form
