Overview
Discussions with herbicide applicators in the agriculture and lawn care industries suggested that the addition of nitrogen to the Velpar herbicide solution would increase efficacy of the herbicide and increase growth of desired species. We designed this simple field trial to test that idea.
Pre-treatment stand description and condition
Pre-treatment species composition:
Pre-Harvest stand composition – 37% Jack Pine, 20% Red Pine, 26% Dead Jack Pine, 16% Balsam Fir, 6% White Spruce, 3% Aspen, 2% Misc. The stand was in a transition period where the Jack Pine was declining.
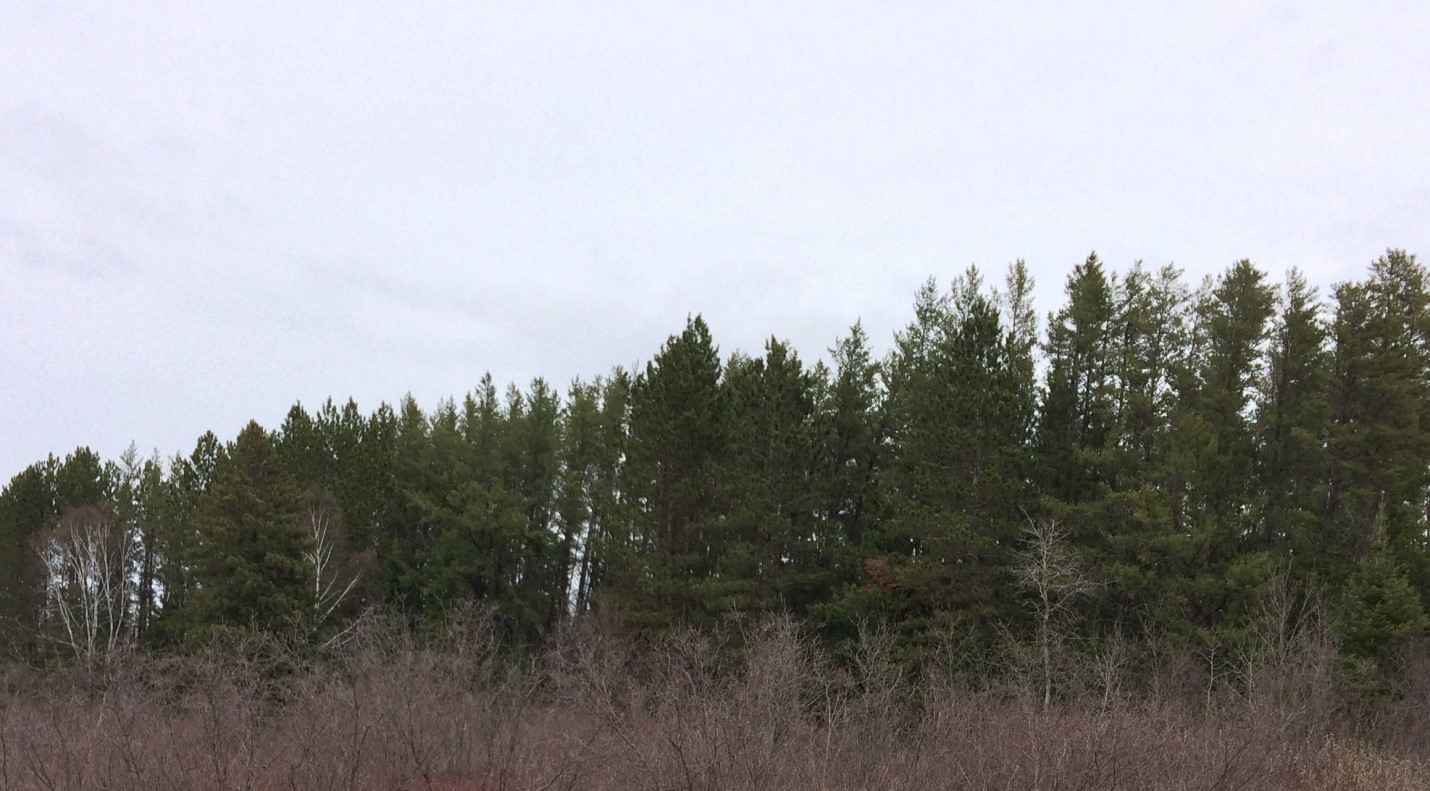

Figure 1: Velpar + N Trial preharvest photo
Silviculture Prescription
The prescription for this site was to clearcut the site, reserving White Pine and Oak, then regenerate the site to Red Pine.
What actually happened during the treatment
Clearcut harvest and planting: The Timber was harvested the summer of 2012. The slash treatment was full tree skid and pile slash. Site was harvested with feller buncher, skidder, limbed with chainsaws and cut to length on landing with a slasher.
The site was broadcast sprayed with 2 quarts Forestry Garlon XRT in June 2013 and Disc trenched the fall of 2013. In April 2014 the site was planted with Red Pine at a rate of 760 seedlings/ac. Seedlings were bud capped the fall of 2014.
Velpar and N application: A contractor was hired to apply herbicide with backpack sprayers in the spring of 2015, before budbreak. The site was divided into six blocks as indicated in Figures 1-5 in Photographs. Two blocks were a control with no release treatment. Two blocks had herbicide applied using a backpack sprayer at a rate of one gallon Velpar L per wet acre. Each seedling was individually treated. The herbicide was applied to a 3’X3’ area centered on the seedling. The remaining two blocks had herbicide applied as above but with the addition of half a gallon of urea–ammonium nitrate (UAN) with 28% nitrogen per wet acre.
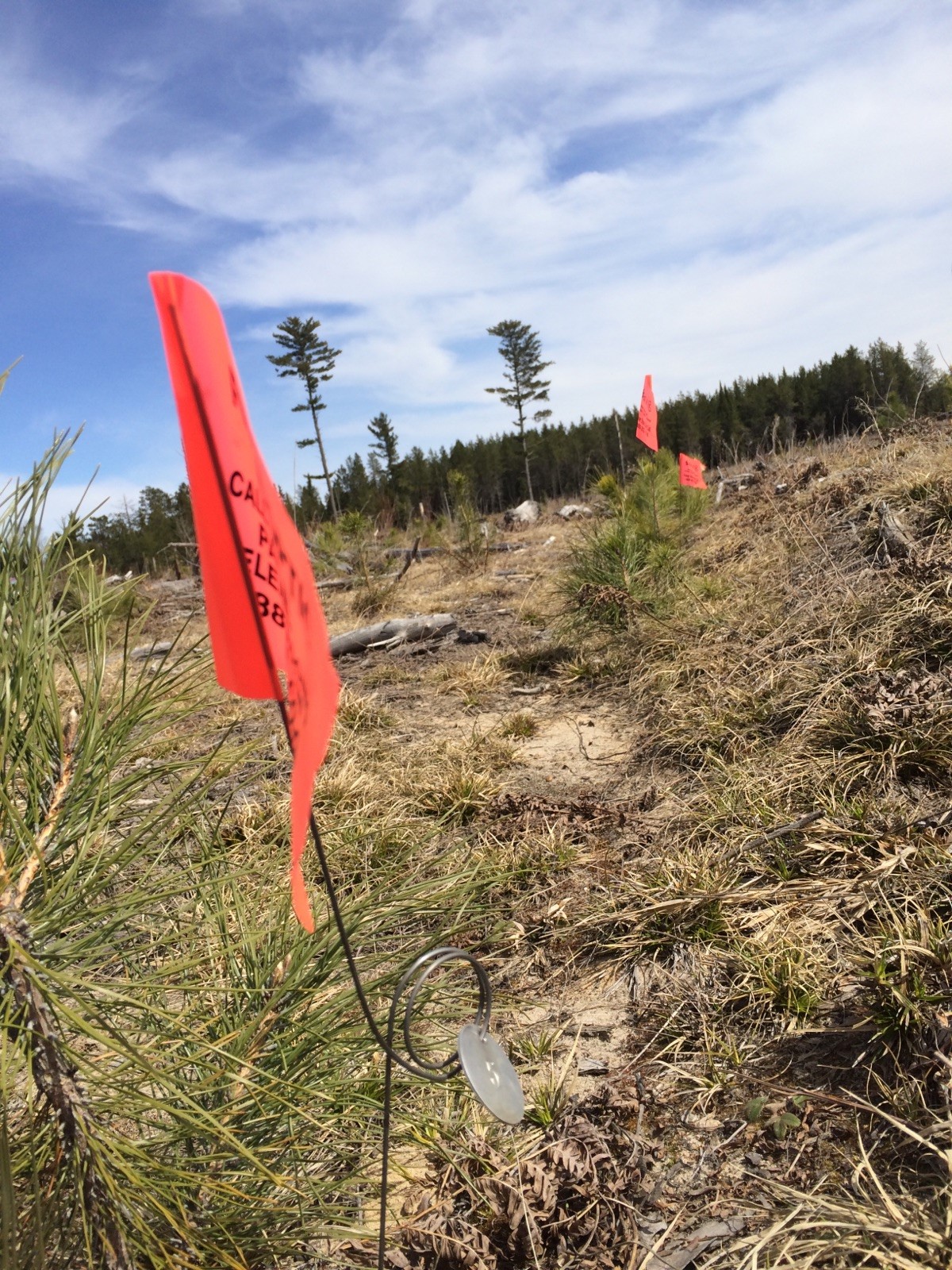

Figure 2: Velpar + N Trial postharvest photo
Post-treatment assessment
Sixty seedlings were selected for monitoring, ten in each block. Seedlings selected were ones with a single terminal leader with no damage.
Seedling height measurements were taken before herbicide application and before bud break in 2015. For consistency, measurements in 2016 and 2017 were taken before bud break.
Hubbard Co. Release Trial - Measurements in inches:
|
2015 Height |
2016 Height |
2015 Growth |
Percent Growth >Control 2015 |
2017 Height |
2016 Growth |
Percent Growth >Control 2016 | Percent Total Height> Control | |
|
Control |
6.4 |
10.4 |
4 |
17 |
7.1 |
|||
|
Velpar |
6.2 |
10.1 |
3.9 |
-2.5% |
18 |
7.8 |
9.9% |
5.9% |
|
Velpar+N |
7.1 |
12.3 |
5.2 |
30.0% |
22.2 |
9.9 |
39.4% |
30.6% |
Mortality and deer browse:
|
Treatment |
Browse 2015 |
Mortality 2015 |
|
Control |
4 |
0 |
|
Velpar |
1 |
2 |
|
Velpar+N |
0 |
1 |
There was no herbivory of monitored seedlings in 2016. The only mortality in 2016 was from a truck running over one seedling
Plans for future treatments
The goal for this site is to grow Red Pine to an average DBH of 22 inches before the next final harvest. Intermediate goals to get to the final goal are:
The first thin will take place around 30 years old when the stand has 500-550 trees per acre with an average DBH of 7.5 inches and a BA of 150. Subsequent thinnings will occur when stocking levels reach the A line in the stocking chart for Red Pine until final harvest.
Costs and economic considerations
|
Item |
Income |
Expense |
|
Timber sale revenue |
$69,362.05 |
|
|
Set up and administer timber sale |
|
$1,000.00 |
|
Site prep |
|
$8,303.50 |
|
Planting |
|
$5,802.50 |
|
Bud capping |
|
$1,912.75 |
|
Release |
|
$3,897.74 |
|
Total |
$69,362.05 |
$20,916.49 |
|
Net |
$48,445.56 |
Of the $20.916.49 of expenses the Nitrogen accounted for only $40.00.
Summary / lessons learned / additional thoughts
The seedlings treated with Velpar + N grew substantially more in the two growing seasons than either the seedlings treated with Velpar only (23.3%) or the control seedlings (30.6%).
It was assumed that the effects of the nitrogen would give added growth to the treated seedlings the first year but the continued increased annual growth showed that the nitrogen made the seedlings stronger and that increased vigor continued into subsequent years
The difference in growth between the Velpar only and the control was not very pronounced and I think it was because the site, being an FDn12b which is quite sterile, has very little competition. Had this been on a site with more competition the results might have been more dramatic. This trial might not provide conclusive evidence of the effects of applying nitrogen during release but it does show that more testing could be done with little additional cost above normal regeneration costs.
Considering the findings of this trial and the minimal additional cost we are adding nitrogen to all of our Velpar release projects. We are also going to do some experimenting with the addition of nitrogen during site prep herbicide applications.
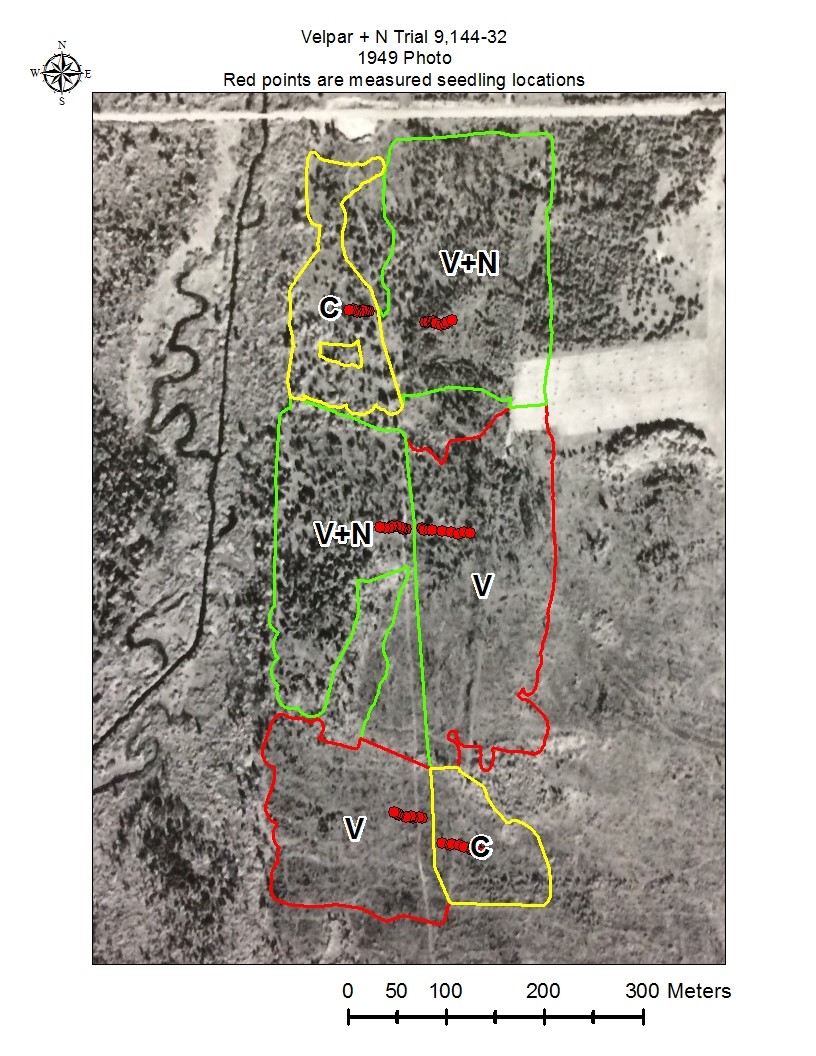

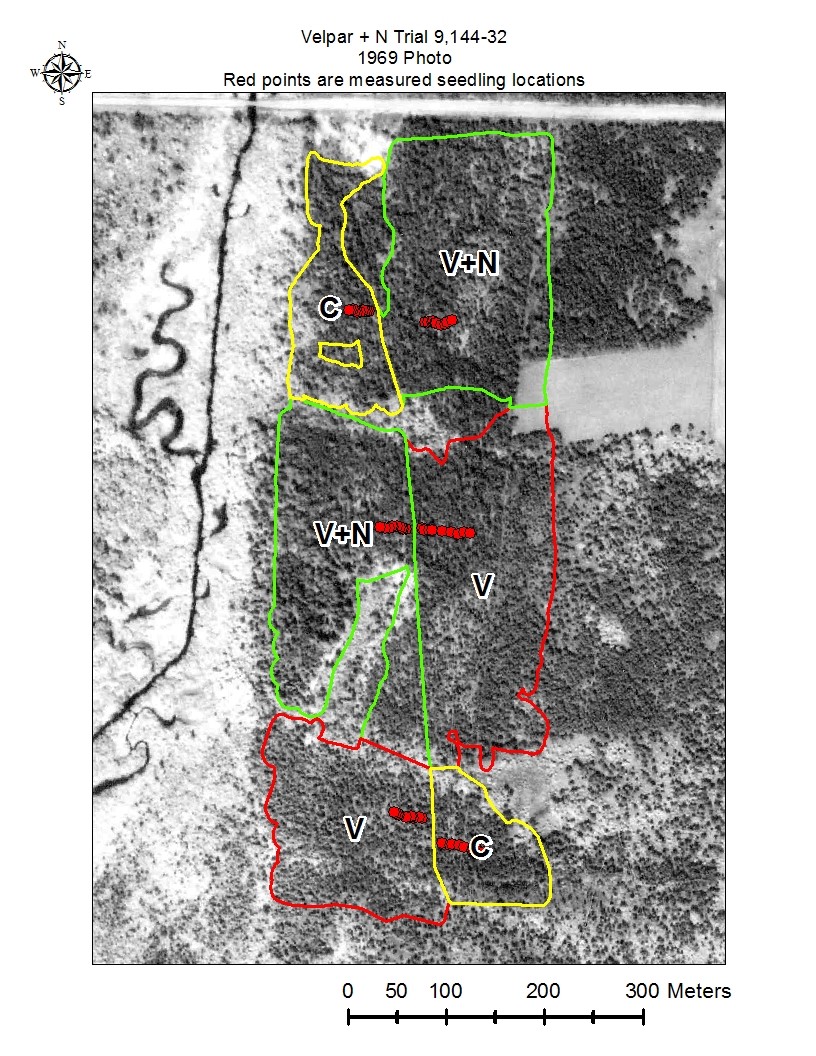
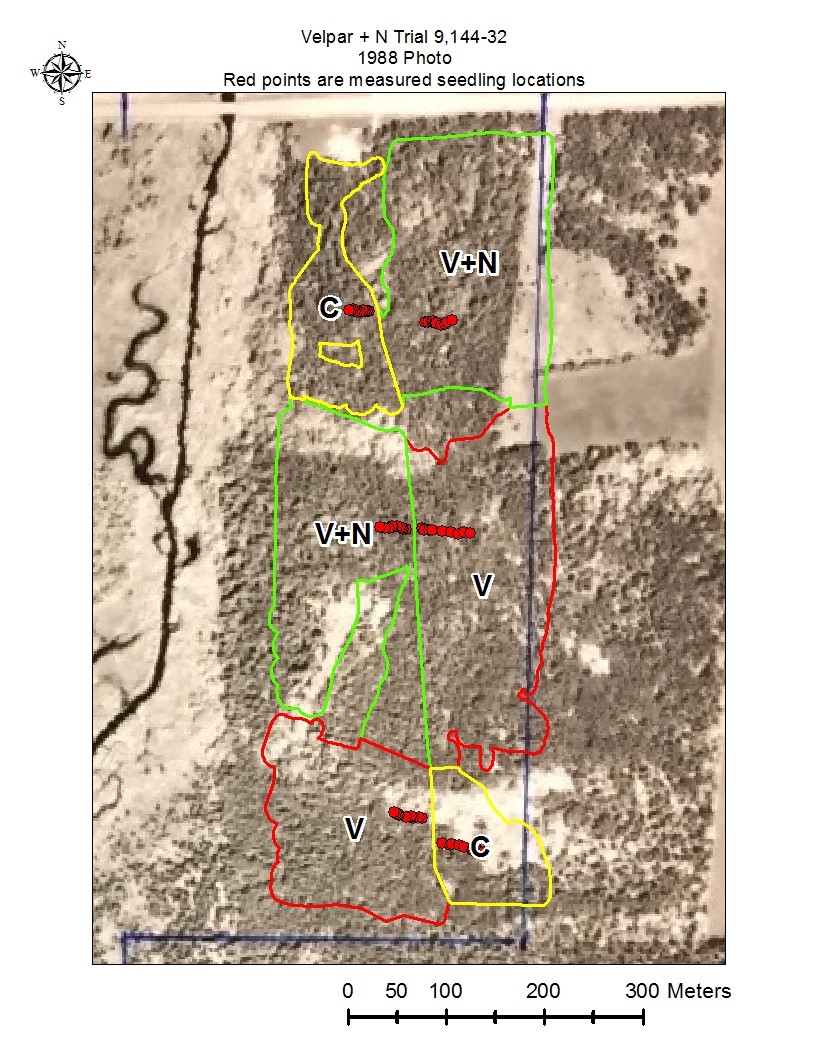
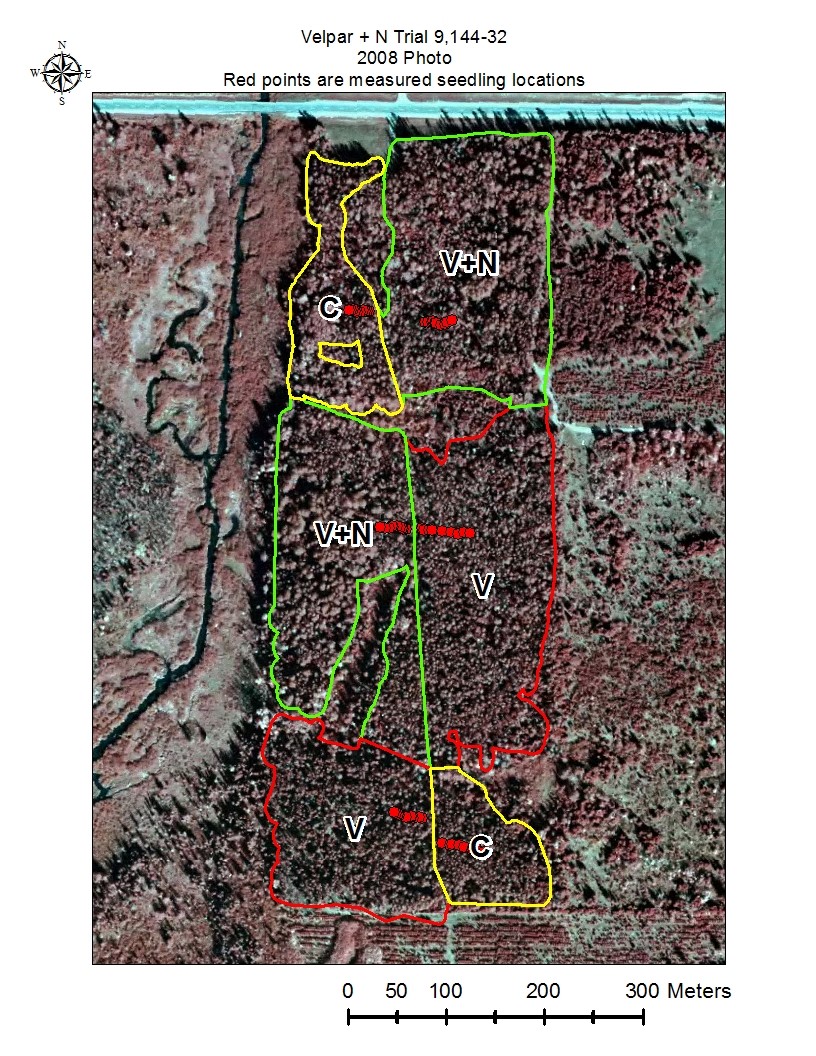
Figures 3 through 6 show the measured seedling locations.
Submitted by
Allen Lysdahl
Allen has worked for Hubbard County since 1994 heading up the artificial regeneration program on Hubbard County Lands.
